00:58
1:40
3:28
3:40
5:13
It is a source of financing for companies from a very early stage of growth (such as startups ) to small, medium and large companies. It is an alternative source of financing to equity, and it is an instrument that usually has a specific maturity.
That is, I lend you money and, in exchange, you pay me a return throughout the life of that loan. Upon its maturity, you return the capital I lent you.
Since it is private debt, it is debt between private actors: investment funds specialising in debt and companies in different stages of growth.
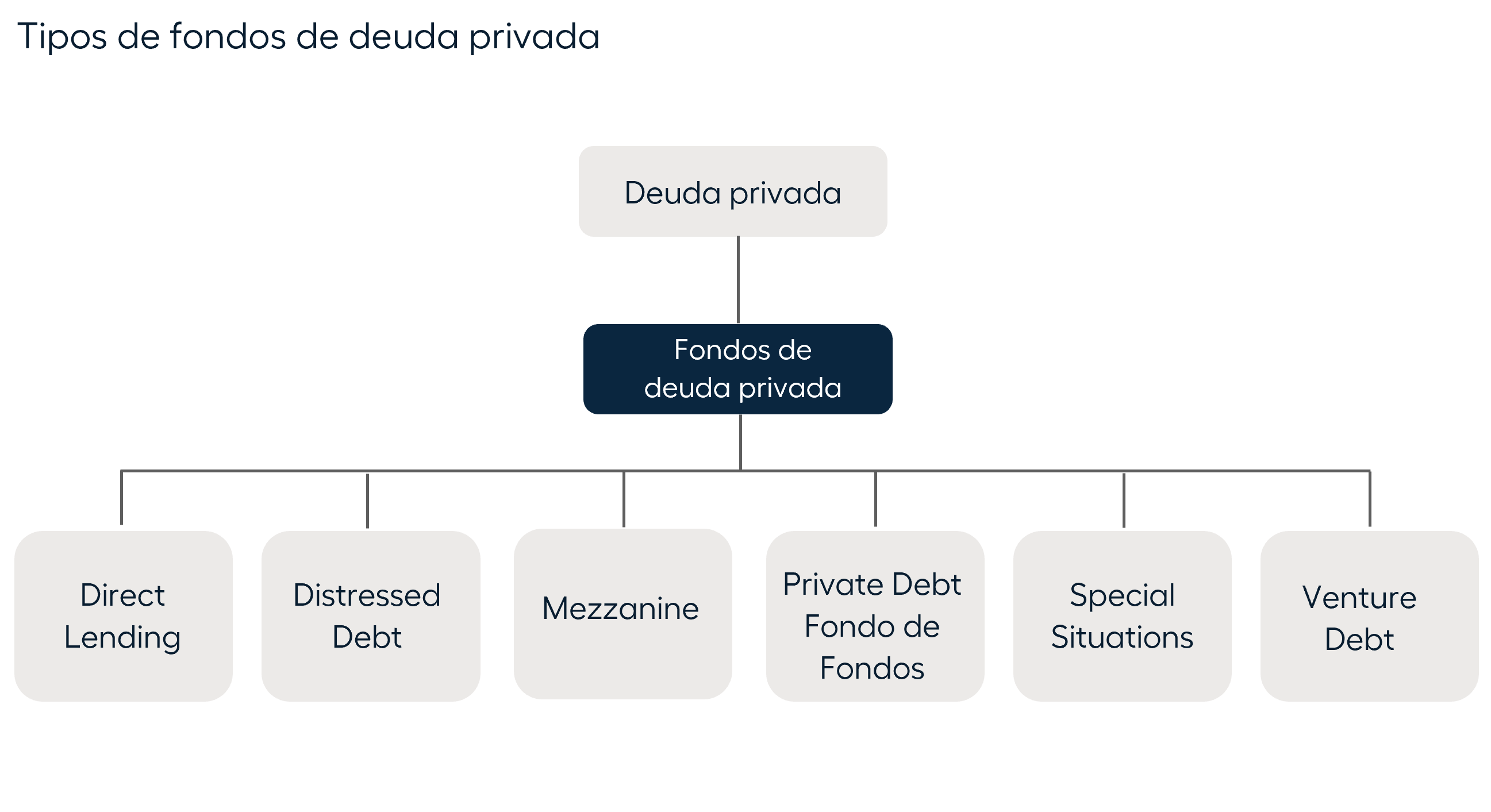
There are different types of strategies according to the risk taken on and to what the funds are allocated, that is, if it is for the organic or inorganic growth of companies or if it is for refinancing purposes.
You seek a certain return based on the risk (where the debt is located in the companies' capital structure).
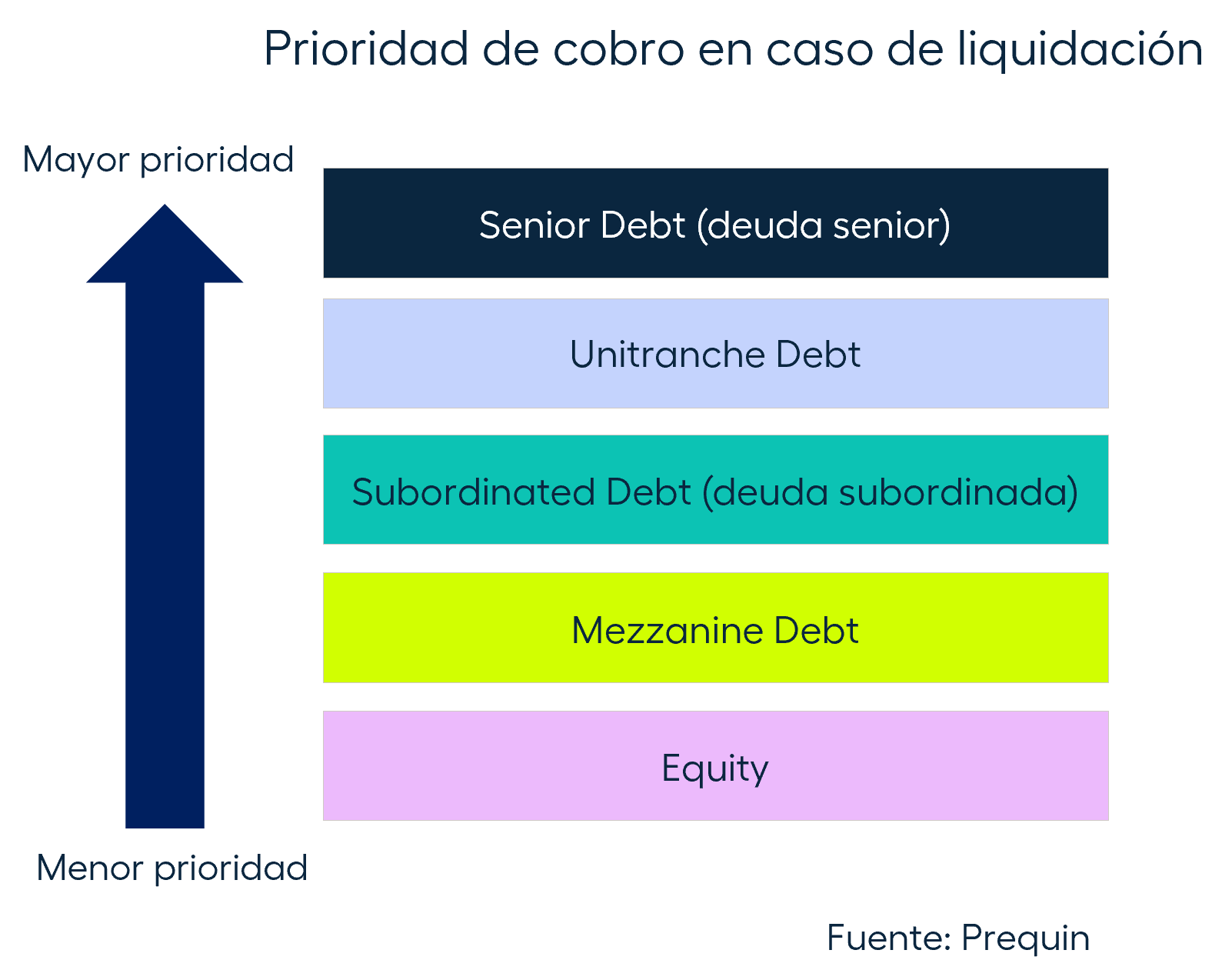
There are several types of private debt, and in order to differentiate them we need to understand how a company's capital is structured. Capital structure refers to the way a company is financed based on the proportion of debt and type of debt and capital on its balance sheet. This defines how and in which order the capital is returned in the event of bankruptcy.
Senior debt is at the top of the capital structure and is returned first, so it has the lowest risk. Equity is at the bottom and is returned last, making it high risk capital.
There are more conservative strategies to preserve capital, in which investors seek to recover the capital in exchange for coupons or the interest rates at which the loan is set, as well as strategies that will seek the capital's appreciation.
In terms of capital preservation two options stand out: Direct lending and Mezzanine.
On the other hand, there are capital appreciation strategies that seek slightly higher returns. There are different strategies for special situations , based on the type of industry or the type of asset to be financed, on the point the company is at and the creditworthiness and on the distressed debt (it seeks returns not only with the payment of coupons, but also by buying the debt issued by the company at a discount; they are usually companies that are in a situation of financial stress).
When you invest in debt, you lend money in exchange for a return. Imagine that I lend it to you with a two-year maturity. During that period, you will pay me an interest, the coupon, and you will pay it to me every month or on a quarterly basis. Upon the loan's maturity, two years later, you will return the capital I lent you.
Although investment in private debt is less risky than other strategies such as equity (because of the priority when it comes to collecting what has been invested if there are any problems in the company), like any investment, it entails different risks:
Investment in private debt has different types of risks that you have to oversee, which is why it is important to always choose management companies or fund managers that understand these risks very well and that have a history of generating attractive returns with their investment strategies.
Investing in private debt has very significant advantages. On the one hand, it is an instrument with little correlation with other capital instruments or public markets.
In addition, there are also mechanisms to hedge against scenarios of high inflation and high interest rates, and sometimes there is collateral against which, if there is a problem in the company, you can collect.
It is a very useful strategy when it comes to supporting and increasing the returns you are looking for in a portfolio where you have stocks, public market bonds, etc. It helps you increase the return of your portfolio without taking on many risks.
The various investment strategies in private debt differ according to the risk taken on and the allocation of the funds
Private debt investment is one of the safest private capital investment strategies
The coupon is the amount returned at the end of the loan's life
When you click on any underlined term, you can see a definition and example of each concept
When you click on any underlined term, you can see a definition and example of each concept
When you click on any underlined term, you can see a definition and example of each concept